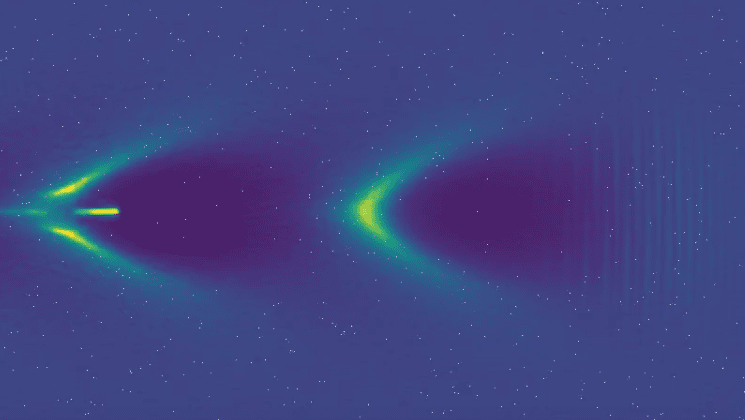
This video shows a simulation of a relativistic laser pulse propagating through a plasma. The plasma density is modulated due to the plasma wake driven by the laser pulse. The imprint of the laser's electric and magnetic filed is still visbile in the front. The while lines visualize traces of inidiviual particles of the plasma. The length of each line corresponds to the position of the particle during the last 5.5 femto seconds. Therefore faster particles have longer lines. Video by Stephan Kuschel.
Graphic: FreepikLasers generate the most extreme fields achievable in the laboratory on mesoscopic and macroscopic spatial scales (only highly ionised heavy ions have higher fields, but on the Angstrom scale). Ultra-intense lasers achieve fields of 1013V/m and greater, alternatively these fields are on the order of 10 MV/µm or 10GV/mm. Particle accelerators using radiofrequency waves typically accelerate particles to MeV to GeV over distances of many metres to kilometres – making the use of laser fields very attractive.
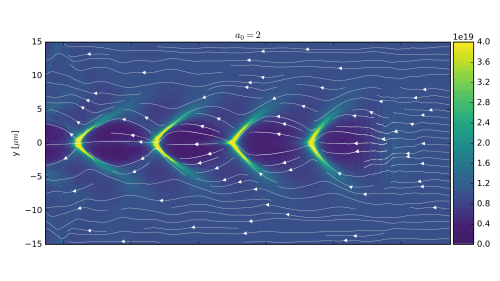
Electron accleration is most efficient if an accelerating field can co-move with electrons over large distances. This is achieved by driving a wakefield (like the wave following a ship) using a powerful laser: The laser expels the electrons in its path (just like a ship pushes away the water) and the electrons feel a force that accelerates them. The figures show simulations of the plasma wave with and without an electron bunch being accelerated (the accelerating bunch is the dot in V-shape).
The Research Team of Target Area 1
Image: Ira WinklerPublications:
- B. Lei, T. Teter, J. W. Wang, et al., "Flexible x-ray source with tunable polarization and orbital angular momentum from Hermite-Gaussian laser modes driven plasma channel wakefieldExternal link," Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 22 071302, (2019)
- S. Kuschel, M. B. Schwab, M. Yeung, D. Hollatz, A. Seidel et al., "Controlling the Self-Injection Threshold in Laser Wakefield Accelerators"External link, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 (15), 154801, (2018)
- B. Lei, J. Wang, V. Kharin, M. Zepf et al., "gamma-Ray Generation from Plasma Wakefield Resonant Wiggler"External link, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 (13), 134801, (2018)
- J. W. Wang, C. B. Schroeder, R. Li, M. Zepf et al., "Plasma channel undulator excited by high-order laser modes"External link, Sci. Rep. 7, 16884, (2017)
- M. Yeung, S. Rykovanov, J. Bierbach, L. Li et al., "Experimental observation of attosecond control over relativistic electron bunches with two-colour fields"External link, Nat. Photonics 11 (1), (2017)
- S. Kuschel, D. Hollatz, T. Heinemann, O. Karger et al., "Demonstration of passive plasma lensing of a laser wakefield accelerated electron bunch"External link, Phys. Rev. Accel. 19 (7), 071301, (2016)